The opening or closing of control valves is done by means of electrical, hydraulic or pneumatic systems. Positoners are used to control the opening or closing of the actuator based on Electric, or Pnuematic Signals. These control signals, traditionaly based on 3-15psi (0.2-1.0bar), more common now are 4-20mA signals for industry, 0-10V for HVAC systems, & the introduction of "Smart" systems, HART, Fieldbus Foundation, & Profibus being the more common protocols.
Types of control valve
Control valves may be categorized as below:
o Conventional valve
o Severe service valve
o Pressure independent control valve
Types of control valve bodies
The most common and versatile types of control valves are sliding-stem globe and angle valves. Their popularity derives from rugged construction and the many options available that make them suitable for a variety of process applications, including severe service. Control valve bodies may be categorized as below.
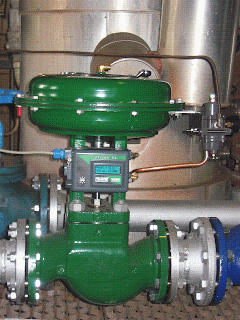
Globe control valve with pneumatic actuator and smart positioner
* Angle valves
o Cage-style valve bodies
o DiskStack style valve bodies
* Angle seat piston valves
* Globe valves
o Single-port valve bodies
o Balanced-plug cage-style valve bodies
o High capacity, cage-guided valve bodies
o Port-guided single-port valve bodies
o Double-ported valve bodies
o Three-way valve bodies
* Rotary valves
o Butterfly valve bodies
o V-notch ball control valve bodies
o Eccentric-disk control valve bodies
o Eccentric-plug control valve bodies
0 comments:
Post a Comment